Business owners, HR managers, and payroll administrators in Singapore face a tricky task when it comes to overtime calculations. It’s not just about fair pay — it’s about following rules, building trust, and keeping employees motivated. Mistakes can lead to penalties unhappy staff, and ongoing arguments. Getting it right can boost employee loyalty and ensure you stick to the law.
This guide breaks down how to figure out overtime pay in Singapore under the Employment Act. You’ll find real-world examples common pitfalls to avoid, and ways to make the process easier using payroll software.
Who Can Get Overtime Pay in Singapore?
The Employment Act doesn’t cover every employee for overtime. The Ministry of Manpower (MOM) in Singapore says:
- Employees making up to SGD 2,600 a month (or SGD 4,500 a month for non-workmen) have coverage.
- Manual employees (workmen) earning up to SGD 4,500 a month also have eligibility.
- Managers and executives don’t have overtime protection unless their contracts say otherwise.
In Singapore, employees who make up to SGD 2,600 monthly (or SGD 4,500 monthly for laborers) have the right to get extra pay for overtime work under the Employment Act from MOM.
How to Figure Out Overtime Pay in Singapore
MOM’s way to calculate overtime is simple, but putting it into practice often isn’t easy.
Overtime Pay Formula (MOM):
Hourly Basic Rate × 1.5 × Overtime Hours Worked
Where:
Hourly Basic Rate = (Monthly Basic Salary ÷ 26 days ÷ Daily Working Hours)
1.5 = Overtime multiplier under MOM rules
Example Scenario:
For instance, an admin officer with a monthly salary of SGD 2,400 putting in 44 hours/week. For one week, she worked 6 hours more than usual.
Hourly Basic Rate = SGD 2,400 ÷ 26 ÷ 8 = SGD 11.54
The Overtime Rate = 11.54 × 1.5 = SGD 17.31
Overtime Pay = 17.31 × 6 = SGD 103.86
In Singapore, companies pay overtime at 1.5 times the hourly basic rate for each extra hour worked.
Overtime on Rest Days and Public Holidays
Different rates will apply if an employee works on a rest day or public holiday.
Rest Day:

Source: Ministry of Manpower
Public Holiday:
Payment for work on a public holiday is calculated as follows:
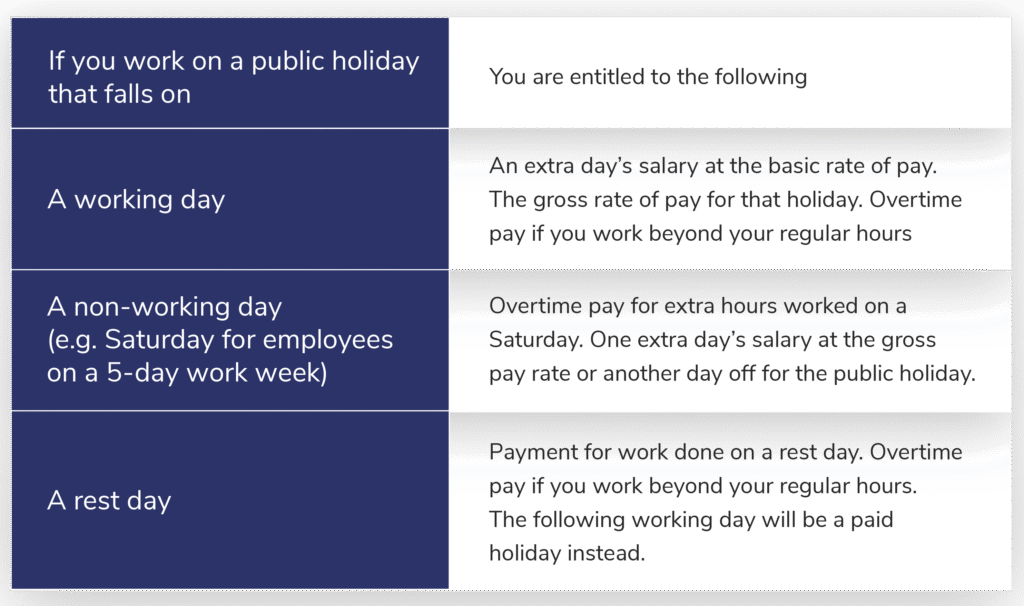
Source: Ministry of Manpower
Remember:
- For employees covered under Part IV: Employers cannot substitute overtime pay with time off; they must compensate it at a rate of at least 1.5 times the hourly basic rate of pay.
- For employees NOT covered under Part IV: Overtime entitlement depends on the terms stipulated in the employment contract.
- Timing of overtime pay: Employers must disburse overtime compensation within 14 days following the end of the salary period during which the employees worked overtime.
Frequent Overtime Pay Errors Made by Employers
- Wrongly labeling employees – thinking managers don’t get overtime when their contracts say they do.
- Missing rest days/public holidays – pay rates might change.
- Errors in manual math – mistakes in Excel sheets cause arguments.
- Breaking MOM rules – risking penalties and affecting the company’s image.
Let’s take an example. Many small businesses find it hard to keep track of time . When they don’t have good systems to manage attendance, overtime records often go missing or spark debates — making both HR and employees unhappy.
The Dangers of Doing Overtime Calculation Manually
A study reveals that 55% of Asian companies still use spreadsheets for payroll. Though familiar, spreadsheets can’t handle complex compliance rules well.
- Mistakes can result in overpaying (affecting profits) or underpaying (inviting legal trouble).
- Payroll teams waste time double-checking figures instead of planning ahead.
- Employees lose faith when their pay doesn’t match their actual work hours.
What’s worse, companies that break MOM’s regulations face fines and penalties — as shown in cases highlighted by Singapore Legal Advice.
Using HRMS & Payroll Software to Automate Overtime
This is where technology comes into play. Up-to-date HRMS and payroll systems like Info-Tech Payroll Software
- Record work hours through biometric or digital attendance.
- Use MOM-compliant overtime calculations.
- Create clear payslips employees can rely on.
- Connect with accounting for smooth financial reporting.
HR leaders can turn their attention to talent management and employee engagement instead of putting out payroll fires.
Wrapping Up: Changing Compliance into Confidence
Overtime pay in Singapore isn’t just something the law requires — it shows how much you value your team. When you handle it right, it builds loyalty, cuts down on disagreements, and boosts your workplace culture.
With Info-Tech Payroll Software, you can stop worrying about mistakes made by hand and put your energy into growing your business with peace of mind.
Want To Make Payroll Simpler? Ask for a Demo Now!
Frequently Asked Questions:
Who can get overtime pay in Singapore?
The Employment Act from MOM covers employees making up to SGD 2,600 a month. For workmen, this limit goes up to SGD 4,500 a month.
How much is overtime pay in Singapore?
Employees get 1.5 times their normal hourly rate for each extra hour they work.
How do you figure out the hourly basic rate?
Take the monthly basic pay, divide it by 26 days then divide that by the number of hours worked in a day.
Are managers and executives able to claim overtime pay?
No. But if their job contract says they can get overtime then they might be able to claim it.
How can companies make overtime pay calculations easier?
By using HRMS and payroll software that has an impact on automating MOM-compliant overtime rules ensuring correctness and reducing time spent.

